Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it? This respiratory virus, similar to RSV and influenza, is causing concern. Let’s explore what HMPV is, its symptoms, and why it’s impacting so many children in China right now. We’ll cover diagnosis, treatment, and importantly, prevention strategies to keep your kids healthy.
So, HMPV is hitting kids hard in China right now – it’s a respiratory virus, kinda like RSV. Completely unrelated, but while we’re on news, check out this sports update: O’s agree to 1-year deal with veteran SP Charlie Morton. Anyway, back to HMPV; it’s causing concern because of its spread among young children, highlighting the need for vigilance and preventative measures.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus, particularly affecting young children. It spreads easily, much like the flu, through coughing and sneezing. While most infections are mild, some can lead to serious complications like pneumonia or bronchiolitis, especially in vulnerable children. The recent surge in cases in China highlights the importance of understanding this virus and taking preventative measures.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) in Children: An Overview
The recent surge in Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases among children in China highlights the importance of understanding this respiratory virus. This article provides a comprehensive overview of HMPV, including its characteristics, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and the implications of the current outbreak.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): Structure, Genotypes, and Transmission
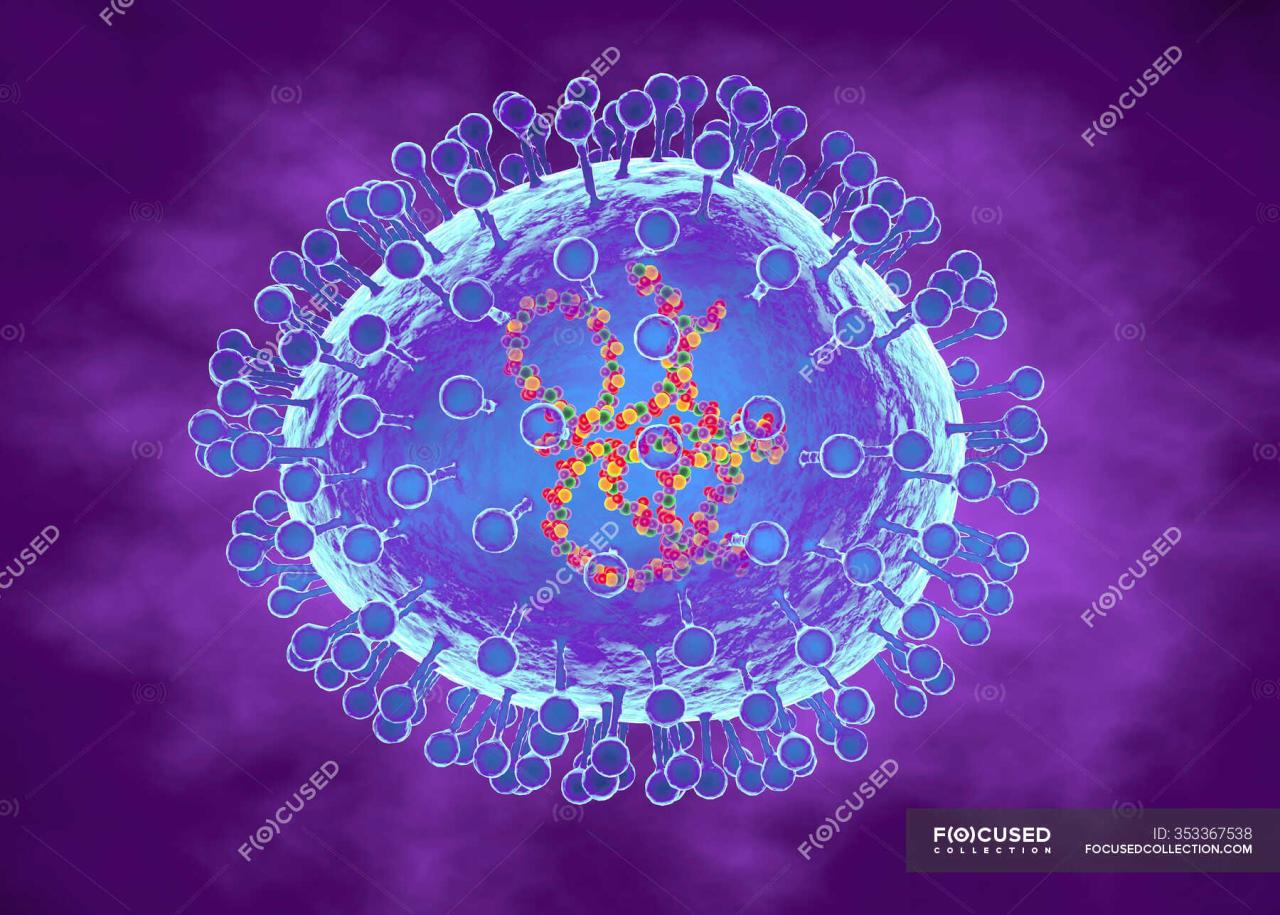
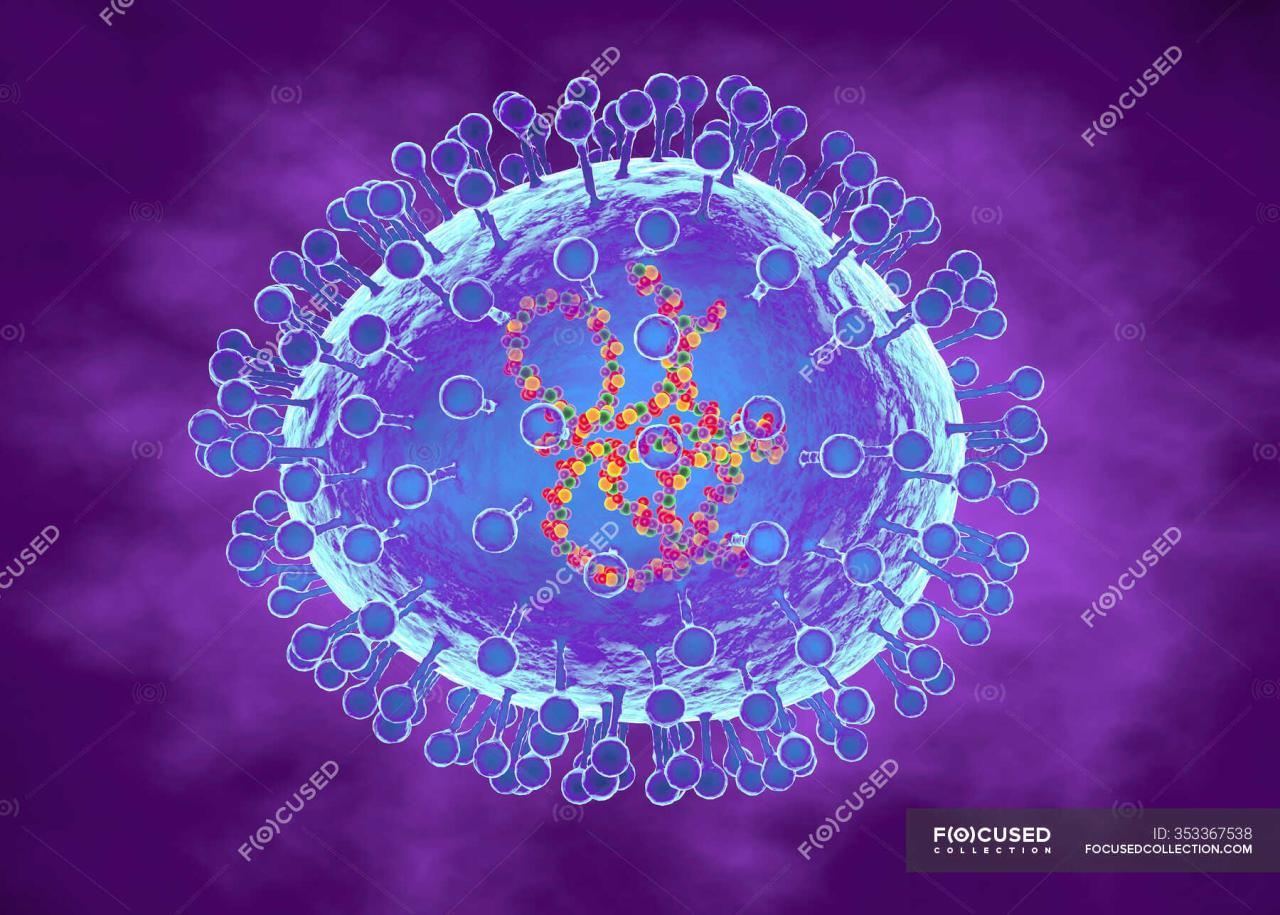
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family. Its structure is similar to other paramyxoviruses, with a single-stranded RNA genome encased in a lipid envelope containing surface glycoproteins. These glycoproteins, particularly the fusion (F) and attachment (G) proteins, play crucial roles in viral entry and infectivity. HMPV is classified into two major genotypes, A and B, with further sub-lineages exhibiting genetic diversity.
Genotype A infections are often reported more frequently than genotype B. HMPV is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets produced during coughing or sneezing, with close contact being a major factor in spread.
HMPV Compared to Other Respiratory Viruses
HMPV shares similarities with other common childhood respiratory viruses, such as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and influenza. However, there are also key distinctions. While all three viruses cause respiratory illness, the severity and specific symptoms can vary. For instance, bronchiolitis is a more common complication of RSV and HMPV than influenza.
| Symptom | HMPV Severity | HMPV Frequency | RSV Severity | RSV Frequency | Influenza Severity | Influenza Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cough | Mild to Severe | High | Mild to Severe | High | Mild to Severe | High |
| Runny Nose | Mild to Moderate | High | Mild to Moderate | High | Mild to Moderate | High |
| Fever | Mild to Moderate | Moderate | Mild to Moderate | Moderate | Mild to High | Moderate |
| Wheezing | Mild to Severe | Moderate | Mild to Severe | High | Mild to Moderate | Low |
| Bronchiolitis | Possible | Moderate | Possible | High | Less Common | Low |
| Pneumonia | Possible | Low | Possible | Moderate | Possible | Moderate |
Symptoms and Severity of HMPV Infection in Children
HMPV infection in children typically presents with symptoms similar to other common respiratory illnesses. These can range from mild upper respiratory symptoms like runny nose and cough to more severe lower respiratory tract infections, including bronchiolitis and pneumonia. The severity of illness varies depending on factors such as the child’s age, underlying health conditions, and the specific HMPV genotype.
Infants and young children are generally at higher risk of developing severe disease. Older children may experience milder symptoms.
Risk Factors and Vulnerable Populations
Several factors increase the risk of severe HMPV infection. Premature infants, children with underlying respiratory or cardiac conditions (like asthma or congenital heart disease), and those with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable. Environmental factors, such as overcrowding and poor ventilation, can also contribute to the transmission and spread of HMPV.
- Maintain good hand hygiene.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Ensure adequate ventilation in homes and childcare settings.
- Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces.
- Promptly seek medical attention if symptoms worsen.
Diagnosis and Treatment of HMPV
HMPV infection is typically diagnosed using molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays, which detect the virus’s genetic material in respiratory samples. Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV. Management focuses on supportive care, including hydration, oxygen therapy if needed, and managing symptoms such as fever and cough.
A flowchart illustrating the diagnostic pathway for a child presenting with respiratory symptoms would start with an assessment of symptoms. If lower respiratory symptoms are present, further investigations such as a chest X-ray might be conducted. If the clinical picture suggests a viral infection, a PCR test for common respiratory viruses, including HMPV, would be ordered. Treatment would then be based on the specific diagnosis and severity of the illness.
The Current Outbreak in China: Contributing Factors
The recent rise in HMPV cases in China may be attributed to several factors, including reduced immunity following the COVID-19 pandemic, increased social interaction after easing of restrictions, and potentially circulating strains with higher transmissibility. Strengthened public health surveillance, improved infection control measures in healthcare settings, and public health communication campaigns play crucial roles in mitigating the spread. Comparing this outbreak with previous ones requires analysis of epidemiological data, including the geographic distribution, severity of illness, and the impact of public health interventions.
Worried about the HMPV viral outbreak hitting Chinese kids? It’s a serious respiratory illness, so staying informed is key. Need a break from the news? Check out the confirmed starting line-ups for today’s big game: Confirmed line-ups | Spurs vs Newcastle. Then, get back to researching HMPV prevention measures – knowing the symptoms and best practices can really help protect your family.
An illustrative map depicting the geographical spread of HMPV cases in China during the outbreak would likely use a choropleth map, with different colors representing varying levels of infection rates across different provinces or regions. The map would visually highlight areas with higher case concentrations, potentially revealing patterns of transmission and informing targeted public health interventions. The data visualization would likely include a legend explaining the color scheme and possibly an inset map of China for geographical context.
Prevention and Public Health Strategies, Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it?
Preventing HMPV transmission relies on implementing effective infection control measures. These include promoting hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette (covering coughs and sneezes), and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. While there is currently no licensed HMPV vaccine, research is ongoing to develop effective vaccines. In healthcare settings, robust infection control practices are crucial to prevent nosocomial spread.
- Practice frequent handwashing.
- Cover coughs and sneezes.
- Avoid close contact with ill individuals.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces regularly.
- Promote vaccination against other respiratory viruses (influenza).
- Implement strict infection control protocols in healthcare settings.
- Promote public awareness campaigns on HMPV prevention.
Closing Notes: Viral Disease HMPV Is On The Rise Among Kids In China — What Is It?
The rise of HMPV infections in China underscores the need for increased awareness and proactive public health measures. While HMPV is not new, its recent surge emphasizes the importance of good hygiene practices like frequent handwashing and seeking medical attention for respiratory symptoms. Understanding the virus, its symptoms, and risk factors empowers parents and healthcare professionals to effectively protect children and manage outbreaks.
Staying informed and taking preventative steps are key to mitigating the impact of HMPV.
FAQ Summary
Is HMPV contagious?
Yes, HMPV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
How long does HMPV last?
Most HMPV infections clear up within a week or two, but some can last longer, especially in severe cases.
Is there a vaccine for HMPV?
Currently, there isn’t a widely available vaccine for HMPV, but research is ongoing.
Worried about the rising HMPV cases in China impacting your kids? It’s a good time to be extra vigilant about respiratory illnesses. Hearing about similar health scares, like the one highlighted in this article, Loose Women’s Gloria Hunniford shares how stark doctor’s warning , really emphasizes the importance of staying informed and proactive with your children’s health.
Understanding HMPV and taking preventative measures are key to keeping your little ones safe during this period.
What’s the difference between HMPV and RSV?
Both are respiratory viruses causing similar symptoms, but they are genetically distinct. Doctors use testing to differentiate them.